原题
给你一个 值互不相同 的二叉树的根节点 root 。
在一步操作中,你可以选择 同一层 上任意两个节点,交换这两个节点的值。
返回每一层按 严格递增顺序 排序所需的最少操作数目。
节点的 层数 是该节点和根节点之间的路径的边数。
示例 1 :
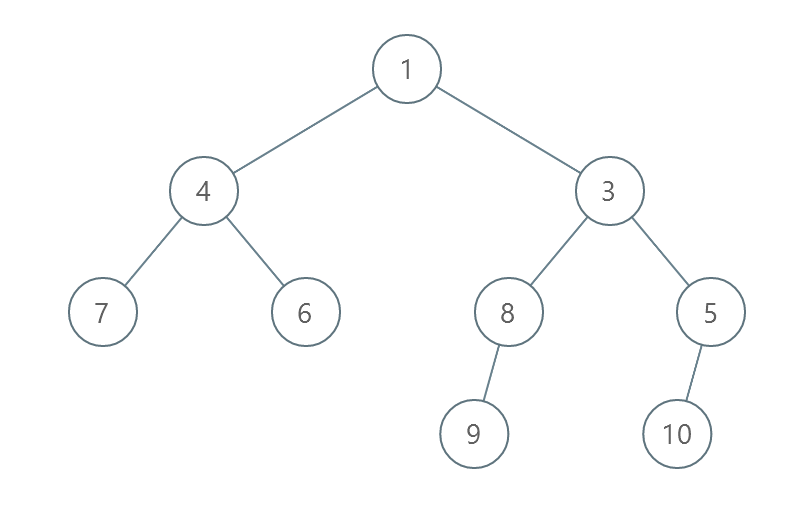
输入:root = [1,4,3,7,6,8,5,null,null,null,null,9,null,10]
输出:3
解释:
- 交换 4 和 3 。第 2 层变为 [3,4] 。
- 交换 7 和 5 。第 3 层变为 [5,6,8,7] 。
- 交换 8 和 7 。第 3 层变为 [5,6,7,8] 。
共计用了 3 步操作,所以返回 3 。
可以证明 3 是需要的最少操作数目。
示例 2 :
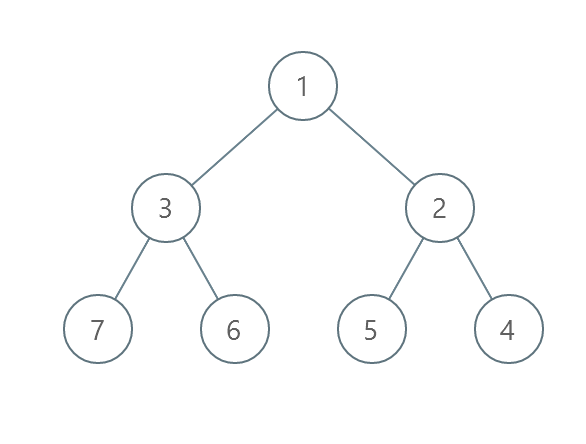
输入:root = [1,3,2,7,6,5,4]
输出:3
解释:
- 交换 3 和 2 。第 2 层变为 [2,3] 。
- 交换 7 和 4 。第 3 层变为 [4,6,5,7] 。
- 交换 6 和 5 。第 3 层变为 [4,5,6,7] 。
共计用了 3 步操作,所以返回 3 。
可以证明 3 是需要的最少操作数目。
示例 3 :
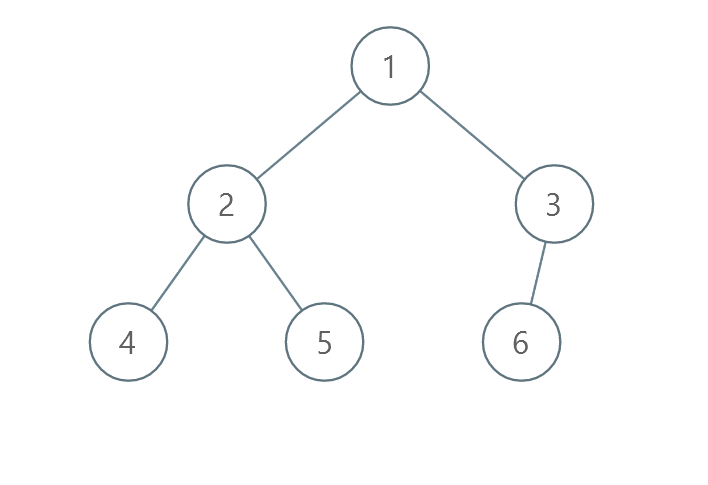
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:0
解释:每一层已经按递增顺序排序,所以返回 0。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 10^5]。 1 <= Node.val <= 10^5- 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
思路
题目要我们将每层的数据排序并找到最少交换次数,很显然,我们可以用二叉树的层序遍历将数据取出来,层序遍历可以使用BFS的思路实现。这里就不多赘述。
但是如何获得最少交换次数呢?
这就需要置换环了,我们可以数据排序前的下标使用一个map保存下来,将数据排序,将其与排序前的位置对比,如果对比到的数据不同,那么代表该数据发生了交换,我们可以沿着数据一路寻找下去,最后会找到自身,成为一个环,那么这个环就是置换环,环内数据依次交换,该环交换次数即得n - 1,找出数组所有的环,将其相加,即可获得总最少交换次数,为数据数据数 - 环数。
用这个思路去结合BFS,即可求得结果。
代码
- leetcode AC片段:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minimumOperations(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
map<int, int> m; // 检测环
queue<TreeNode *> q; // bfs
map<TreeNode*, int> c; // 层数
q.push(root);
c[root] = 1;
int nowC = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
m.clear();
int cnt = 0;
vector<int> before;
while (c[q.front()] == nowC) {
TreeNode* nowNode = q.front();
q.pop();
before.push_back(nowNode->val);
m[nowNode->val] = cnt++;
if (nowNode->left != nullptr) {
q.push(nowNode->left);
c[nowNode->left] = nowC + 1;
}
if (nowNode->right != nullptr) {
q.push(nowNode->right);
c[nowNode->right] = nowC + 1;
}
}
if (!q.empty()) nowC = c[q.front()];
vector<int> after(before);
sort(after.begin(), after.end());
vector<bool> flag(after.size());
int loop = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < after.size(); i++) {
int index = i, num = after[i];
if (!flag[index]) { // 未加入环的情况
while (!flag[index]) {
flag[index] = true;
index = m[num];
num = after[index];
}
loop += 1;
}
}
ans += after.size() - loop;
}
return ans;
}
};
- 为方便本地调试,写了个本地调试片段(建树),用
-1代表了null
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int minimumOperations(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
map<int, int> m; // 检测环
queue<TreeNode *> q; // bfs
map<TreeNode*, int> c; // 层数
q.push(root);
c[root] = 1;
int nowC = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
m.clear();
int cnt = 0;
vector<int> before;
while (c[q.front()] == nowC) {
TreeNode* nowNode = q.front();
q.pop();
before.push_back(nowNode->val);
m[nowNode->val] = cnt++;
if (nowNode->left != nullptr) {
q.push(nowNode->left);
c[nowNode->left] = nowC + 1;
}
if (nowNode->right != nullptr) {
q.push(nowNode->right);
c[nowNode->right] = nowC + 1;
}
}
if (!q.empty()) nowC = c[q.front()];
vector<int> after(before);
sort(after.begin(), after.end());
vector<bool> flag(after.size());
int loop = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < after.size(); i++) {
int index = i, num = after[i];
if (!flag[index]) { // 未加入环的情况
while (!flag[index]) {
flag[index] = true;
index = m[num];
num = after[index];
}
loop += 1;
}
}
ans += after.size() - loop;
}
return ans;
}
};
TreeNode* init(vector<int> nums) {
map<TreeNode*, bool> l, r;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
TreeNode* nowNode = nullptr, *root = nullptr;
for (auto i : nums) {
if (q.empty()) {
auto temp = new TreeNode(i);
root = nowNode = temp;
q.push(nowNode);
} else {
if (nowNode->left == nullptr && !l[nowNode]) {
if (i == -1) {
l[nowNode] = true;
} else {
nowNode->left = new TreeNode(i);
q.push(nowNode->left);
}
} else if (nowNode->right == nullptr && !r[nowNode]) {
if (i == -1) r[nowNode] = true;
else {
nowNode->right = new TreeNode(i);
q.push(nowNode->right);
}
q.pop();
nowNode = q.front();
}
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
Solution s;
vector<int> c({1,4,3,7,6,8,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,9,-1,10});
cout << s.minimumOperations(init(c));
return 0;
}